The world needs UI (User
Interface) and UX (User Experience) designers to ensure that digital products
and technologies are user-friendly, effective, and enjoyable for people to use.
UI (User Interface) and
UX (User Experience) design are both excellent career options with many
opportunities for growth and advancement.
Table of Content
|
Different
Between UX vs UI Designer?
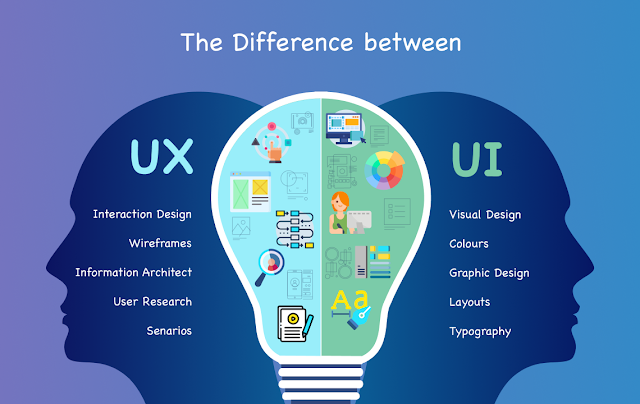
What is User Interface (UI):
UI refers to the visual
elements and design components that users interact with when using a digital
product. It encompasses everything the user sees, touches, clicks on, and
interacts with on the screen.
UI design is concerned with creating an
aesthetically pleasing and visually consistent layout that is easy for users to
navigate and understand.
What is User Experience (UX):
UX refers to the overall
experience a user has when interacting with a product. It focuses on the user's
emotions, perceptions, and interactions throughout their journey with the
product.
UX design aims to create
a seamless, efficient, and enjoyable experience for the user, taking into
account their needs, goals, and preferences.
Main
differences between UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience) design:
| Aspect | UI Design | UX Design |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Visual design, aesthetics, and layout | Overall user experience and satisfaction |
| Scope | Visual design, aesthetics, and layout | Concerned with the entire user journey |
| Elements | Buttons, icons, typography, color scheme | User flows, information architecture |
| Interaction Design | How users interact with visual elements | How users navigate and complete tasks |
| Goal | Create visually appealing and consistent designs | Create meaningful and enjoyable experiences |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Emphasizes the visual aspects of design | Aims to provide a positive emotional response |
| Usability | Deals with the usability of individual elements | Deals with the overall usability and efficiency |
| Accessibility | Considers visual aspects of accessibility | Ensures the product is accessible to all users |
| User Research | Less involved in user research | Conducts extensive user research |
| Design Process | Part of the design process but not the entire process | Encompasses the entire design process |
| Deliverables | Design mockups, wireframes, visual assets | User personas, user journeys, prototypes |
| Team Collaboration | Collaborates closely with UX designers | Collaborates with UI designers and developers |
| End User Interaction | Focused on the surface-level interaction | Focuses on the overall emotional and functional interactions |
| Outcome | Contributes to the product's visual appeal | Contributes to the product's overall success and user satisfaction |
| Examples | Button design, color choices, layout | User flows, wireframes, usability testing |
Actual work of UI Designer
· Visual Design:
UI designers are responsible for the
visual aesthetics of digital interfaces. They create visually appealing designs
that align with the brand's identity and resonate with users.
·
Color and Typography: Selecting
appropriate color palettes and typography that enhance readability and convey
the intended tone of the product.
·
Layout Design:
Organizing the elements on the screen
in a way that is visually pleasing and allows for intuitive navigation. This includes
arranging buttons, menus, and content blocks.
·
Interactive Elements: Designing buttons, icons, forms, and other
interactive components that users will engage with directly.
·
Icon Design:
Creating icons that are clear, recognizable, and convey information
efficiently.
·
Visual Consistency:
Ensuring that design elements are consistent throughout the product to create a
coherent and unified user experience.
·
Responsive Design:
Adapting the design to different screen sizes and devices to ensure a seamless
experience across platforms.
·
Prototyping:
Creating interactive prototypes or mockups to showcase the visual design and
user interactions before development.
·
Collaboration:
Working closely with UX designers, developers, and other team members to bring
the design vision to life.
·
Style Guidelines:
Developing design guidelines or
pattern libraries that outline design principles, components, and usage rules
for maintaining consistency.
Actual work of UX Developer
·
User Research:
Conducting research to understand
user behaviors, needs, motivations, and pain points. This involves methods like
surveys, interviews, and usability testing.
·
User Personas:
Creating detailed user personas that represent different segments of the target
audience to guide design decisions.
·
Information Architecture: Structuring and organizing content and features in a
way that makes it easy for users to find what they're looking for.
·
User Flows:
Designing user flows or paths that users take to achieve specific goals within
the product.
·
Wireframing:
Creating low-fidelity sketches or wireframes to outline the layout and
arrangement of elements on different screens.
·
Prototyping:
Developing interactive prototypes to test and validate the user experience,
interactions, and workflows.
·
Usability Testing:
Conducting usability tests to gather feedback from users and identify areas for
improvement in the user experience.
·
Accessibility:
Ensuring that the product is accessible to users with disabilities, following
accessibility guidelines.
·
Collaboration:
Collaborating with UI designers, developers, and stakeholders to ensure that
the design aligns with user needs and business goals.
·
Iterative Design:
Continuously iterating on the design
based on user feedback and data analysis to refine the user experience.
Why to Choose UI/UX Designing as a Career?
·
High Demand:
As technology becomes more integrated into various aspects of our lives, the
demand for skilled UI/UX designers continues to grow. Companies recognize the
importance of creating user-friendly and engaging digital experiences to stay
competitive.
·
Job Opportunities:
There is a wide range of job
opportunities available for UI/UX designers across industries such as
technology, e-commerce, healthcare, finance, entertainment, and more. This
diversity allows designers to work on projects they are passionate about.
·
Creative Expression:
UI/UX designers have the opportunity
to be creative and innovative while solving design challenges. They get to
combine aesthetics with functionality to create visually appealing and
user-friendly interfaces.
·
Collaborative Work Environment: UI/UX designers
often collaborate with cross-functional teams, including developers, product
managers, marketers, and more. This collaborative work environment allows for
learning from various perspectives and skill sets.
·
Freelance and Remote Opportunities: Many UI/UX
designers have the flexibility to work as freelancers or remotely, giving them
the freedom to choose their projects and work environments.
·
Competitive Compensation: Skilled UI/UX
designers are often well-compensated due to their expertise in creating
valuable and user-centric digital experiences.
·
Global Reach:
With the growth of the internet, the
work of UI/UX designers can have a global impact, reaching users all around the
world.
·
Career Progression:
UI/UX designers can progress from
junior positions to senior roles, lead designers, design managers, and even
start their design studios or consultancies.
How to
Become UI Designer ?
·
Skills:
Proficiency in
design software such as Adobe XD, Sketch, Figma, or Adobe Photoshop.
·
Responsibilities:
Creating icons,
buttons, menus, and other graphical elements.
Ensuring
a consistent and visually pleasing design across different screen sizes and
devices.
Collaborating with
UX designers to create a seamless user experience.
Understanding
design principles and current design trends.
·
Career Path:
UI designers can start as junior designers or interns and work their way up to senior UI designer roles.
They may also specialize in specific industries or design areas, such as mobile app UI design, web UI design, or game UI design.
How to Become UX Developer ?.
·
Skills:
Conducting
user research through surveys, interviews, and usability testing.
Creating
user personas and journey maps to understand user behavior.
·
Responsibilities:
Designing
wireframes and interactive prototypes to visualize the user flow.
Collaborating
with UI designers and developers to bring the product to life.
Advocating
for user-centered design and ensuring accessibility for all users.
·
Career Path:
UX designers often
start as UX researchers or junior UX designers. As they gain experience, they
can move into more senior roles, such as lead UX designer or UX design manager.
Some may also
specialize in areas like information architecture, interaction design, or usability
testing.
Demand of UI/UX Designer
Here are a few reasons
why the demand for UI/UX designers has significantly increased:
Digital Transformation: Businesses across industries are undergoing digital
transformation to enhance their online presence and provide digital solutions
to customers. UI/UX designers play a crucial role in creating user-friendly and
engaging digital experiences.
Mobile and Web Applications: With the
proliferation of smartphones and the increasing reliance on web applications,
there's a growing need for intuitive and visually appealing interfaces. UI/UX
designers ensure that these applications are easy to navigate and use on various
devices.
E-Commerce:
The rise of online shopping and
e-commerce platforms has heightened the importance of creating compelling and
user-centric interfaces to drive sales and improve the overall shopping
experience.
Healthcare and Wellness: Digital health
solutions, telemedicine platforms, and wellness apps require intuitive design
to ensure that users can easily access and manage their health information.
Remote Work and Learning: The shift towards
remote work and online learning has led to an increased demand for
user-friendly communication and collaboration tools, where UI/UX designers play
a critical role in optimizing these experiences.
Entertainment and Media: Streaming
services, gaming platforms, and content-sharing apps rely on UI/UX designers to
create immersive and enjoyable experiences for users.
Smart Devices and IoT: As more devices
become connected through the Internet of Things (IoT), the need for intuitive
interfaces to control and interact with these devices is paramount.
Accessibility and Inclusion: Designing products
that are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, is a
growing concern. UI/UX designers are central to ensuring products are designed
with inclusivity in mind.
Data-Driven Design:
UI/UX designers are leveraging data
and analytics to make informed design decisions, resulting in more personalized
and tailored experiences for users.
Startups and Innovation: New startups and innovative companies are emerging
regularly, seeking UI/UX designers to help create unique and user-centric
products that stand out in the market.
Global Reach:
The internet allows products to reach
a global audience. Effective UI/UX design is essential to cater to the diverse
needs and cultural differences of users worldwide.
Similarities
Between UI and UX?
UX and UI are two related principles of
design even though they are different from each other. The following are some
of the similarities between the two:
- Design Thinking: Both
UX and UI are focused on design. They follow UI UX principles to
come up with the most user-friendly user design possible.
- Aware of User Needs: While
UX is based on the user journey, UI is based on making easy navigation
possible for the users. Both UX and UI have to be aware of the user’s
needs to be able to do that.
- The goal of Delivering a Product That Delights
the Users: UX
and UI have the same goal, to make sure the users are happy with the
product.
Conclusion
In summary, while UI
focuses on the visual and interactive elements of a product, UX is concerned
with the overall quality of the user's experience, encompassing usability,
emotions, and interactions. Both UI and UX are essential for creating products
that are not only visually appealing but also user-friendly, intuitive, and
capable of meeting user needs effectively.

.png)
.png)
.png)